
Jonathon
Fire Escape
Educational and VR Game Design
Project Name: Fire Escape
Team Members: Designer: TianYi Gu
Programmer: Jonathon Song
Technical Artist: Jonathon Song
Material used: Unity, HTC Vive VR Glass
Interactive mode: VR Immersive Experience
Creative concept
Based on the "Internet + BIM + VR", the program demonstrates the visual fire protection in an underground garage in the park. In the era of big data, the Internet has enabled massive amounts of building information to be processed and utilized efficiently. The VR project in Unity3D allows the user to have an immersive experience of escaping from fire.
Project Demonstration
Mode selection
In the mode selection page, the user has two options: novice mode and free mode.
In the novice mode, the system will conduct fire science education and introduce the fire module in the common building to help the user understand each module's roles and improve the escape efficiency in the building fire.
In the free mode, the user can exercise the fire escape by using the fire knowledge in the novice mode so that they can react quickly in the fire and save themselves.


Operation introduction
On the operation introduction page, users will understand how the handles are used to help users have a better experience in the system.
Module tips
In the page of module tips, the introduction of the module that helps people escape from fire will pop up when the user approaches the module.


Score system
After the user escapes successfully, the system will score according to the time taken by the user to escape and the amount of blood remaining. On this page, users can also learn about their deficiencies by viewing the tips and learn to escape the fire faster.
Screenshot picture









Prototype design
Mode selection

Players can choose to join the game in novice mode or free mode.
The novice mode will give the player appropriate prompts and knowledge of the fire safety of the science.
The free mode will bring the player an immersive experience.
Novice mode
In the novice mode, I guide the player according to the order of escaping of the real building fire.
Introduction of operation
Message notification
Introduction of temperature bar



Introduction of smoke alarm
Introduction of time frame
Introduction of life value



Introduction of spray
Introduction of evacuation lighting
Introduction of induction fan



Introduction of fire shutter door
Introduction of smoke machine
Introduction of smoke prevention



Introduction of fire hydrant
Introduction of exit


Rating page

After the player finishes the escape, the player is evaluated according to the time spent by the player in the escape process and other applications of escape knowledge.
Flow chart
Start
Novice Mode
In the novice mode, the player's path and the science knowledge of the fire are guided according to the order of electromechanical operation in the building fire.
UI Introduction
Introduce the blood strips, temperature bars, timers, and handle operations in the scene.
Alarm System
By adding an alarm sound to the system, children can react to the first time they hear the alarm, avoiding confusion.
Score
Through environmental simulations, children can remain calm in a sudden dark environment, looking for and escaping from danger according to the direction of evacuation lighting, and achieving the goal of being able to leave quickly in a similar environment in the future.
Exit
Through environmental simulations, children can remain calm in a sudden dark environment, looking for and escaping from danger according to the direction of evacuation lighting, and achieving the goal of being able to leave quickly in a similar environment in the future.
Ventilation System
Lighting System
Help children learn simple escape techniques such as bending and pouting in the system, making them a subconscious reaction, so that children can reduce the damage caused by smoke in the fire escape.
Through environmental simulations, children can remain calm in a sudden dark environment, looking for and escaping from danger according to the direction of evacuation lighting, and achieving the goal of being able to leave quickly in a similar environment in the future.
Sketch Design
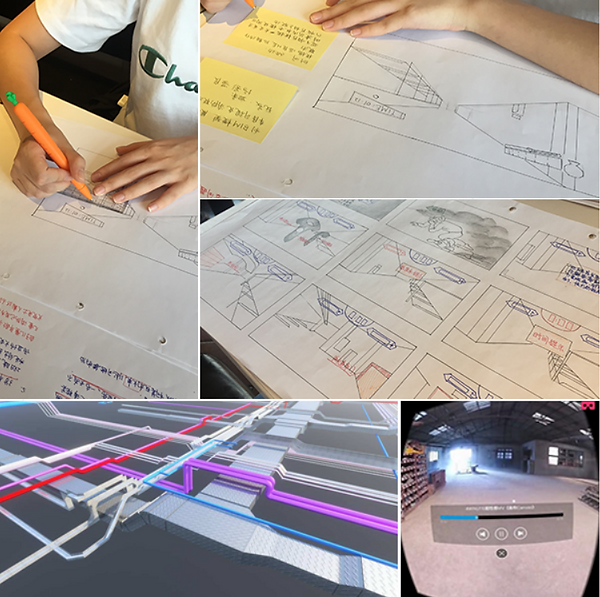
Programming by Playmaker(Unity)



Play Test live picture
![20181024_171701[00_03_46][20190702-18291](https://static.wixstatic.com/media/feec59_22cefffaa8ae4666a71e4d8d10fa5339~mv2.png/v1/fill/w_196,h_336,al_c,q_85,usm_0.66_1.00_0.01,enc_avif,quality_auto/20181024_171701%5B00_03_46%5D%5B20190702-18291.png)
![20181024_171701[00_04_14][20190702-18293](https://static.wixstatic.com/media/feec59_d70a45b589864a9183b7f2cc011d2f72~mv2.png/v1/fill/w_191,h_336,al_c,q_85,usm_0.66_1.00_0.01,enc_avif,quality_auto/20181024_171701%5B00_04_14%5D%5B20190702-18293.png)
Market Research
Age under 18

Survey of deaths from fire accidents in China in 2017
Current status of fire education
In all fire accidents, 20% to 25% of the victims are children. In the past five years, a total of 1,624 minors under the age of 18 have been killed in the fire, accounting for 18.6% of the total number of people killed in the fire.
Lack of safety fire supervision
According to the Global Child Safety Network survey, nearly 40% of children have had at least one burn in their daily lives. More than 30% of children can easily get ignition equipment such as matches and lighters at home. 40% of students have a fire experience.
Weak fire awareness
The National Fire Safety Common Sense Awareness Survey reflects that the survey on the awareness of fire safety awareness of children and adolescents under the age of 17 is only 51.54, which is lower than the average score of 66.80, which is at the lowest level of all ages, and 37.01% of the students are not. I have thought about the fire escape problem.
The causes of child fire safety accidents are multifaceted.
· Parents and schools have low fire safety awareness, leading to omissions and formalization of fire safety education.
· Many parents have never had a fire safety education for their children.
· Schools often think that they have to carry out safety education and exercises for students after accidents happen.
· In order to cope with superior inspections in some schools, fire safety education is completely in the form.

Child fire casualties
Children's ability to escape from self-rescue is weak and easy to casual. Because of their young age, children are physically and mentally weak when the disaster is steep and their lives are threatened. There are even some residents who like to lock their children in the house when they go out to be unattended. If there is a fire, the consequences are unimaginable. Children are the key victims of fire damage, but they lack the common sense of firefighting and self-rescue. How to improve children's fire safety awareness is a major problem faced by the society.
Expert Interview

Counselor: Lu Bai
Introduction: National secondary counselor, psychoanalytic consultant, family therapist.
She is good at family education, youth psychological growth, and other consulting services.
In order to understand how to help children to carry out fire safety education efficiently, I made an appointment with a child psychologist, Bai Hao. My project is aimed at children. There are suggestions on the age group and the way of education.

Fire squadron leader: Yuanchun Zhu
Introduction: The squadron leader of the Songjiang New Town Squadron.
He has been involved in the first-line work of fire protection for more than 15 years. He has extensive experience in fire protection and is responsible for fire safety education in subordinate streets and schools.
In order to further understand the professional knowledge of fire safety and how to correctly educate children's fire safety education, I went to the Songjiang New Town Fire Squadron to discuss with the team leader on March 26, 2018.
The development of fire safety habits
On November 9th, 2017, China Fire Safety Publicity Day, I participated in the Children's Fire Science Popular Science Activities organized by the Shanghai Fire Bureau and discussed how to help children develop good fire safety habits. After interviewing the advice of the Bai Yu consultant, it can be summarized as the following two points:
The best age group
Psychological research data shows that there is an optimal period for the development of habits, and preschool is undoubtedly the best time to develop good fire safety habits for children. Once grown up and even grown up, people's thoughts and behaviors are mature and stable, it is difficult to change and reshape, and the ability to accept and remember new things will also decline. Therefore, preschool education and awareness of safety knowledge is critical.
Multi-party participation in multiple ways in parallel
Regardless of the child's parents, teachers, firefighting functions, or the whole society, they should be aware of the necessity and urgency of conducting safety education at this age. Through storytelling, games, and other means, interesting educational methods enable children to better understand fire safety knowledge and teach them basic fire prevention and escape knowledge in a fun and educational way.
Key points of children's fire education
In the interview on March 26, 2018, I hope the captain told me that there will be some misunderstandings in children's fire education. Many safe escape knowledge for adults and older minors does not apply to children, for example: dial 119, complex Escape surgery, etc., to avoid misunderstandings in children's fire education should emphasize the following points:
Leave the fire at the first time
Parents should teach young children to leave the scene of the fire after the fire, do not bring anything, do not care about anything. Call 119 for children's education after the fourth grade, and it is the right thing to notify the fire.
Hold a wet towel on mouth and nose
Parents should teach their children to cover the nose and mouth with a towel after using a fire. Cover the head and upper body with warm and humid quilts and quickly bend over to leave the scene.
Choose a room with water when trapped
Parents can't escape from the fire when they are away from the fire. They should avoid the toilet, kitchen, and other water-filled rooms. They can also go to the balcony to call for help, but be sure not to fall out of the window.
Fire Escape--Rewards
Fire VR system (the prototype of Fire Escape)--
Gold Awards from NATIONAL 3D INNOVATION DESIGN COMPETITION

Fire Escape--Awards from THE 3RD China VR/AR/MR Creation Contest
